At Sentient Digital, we apply a series of management threads and industry best practices from both the private and government sectors to deliver effective and efficient digital solutions to our clients.
How We Work
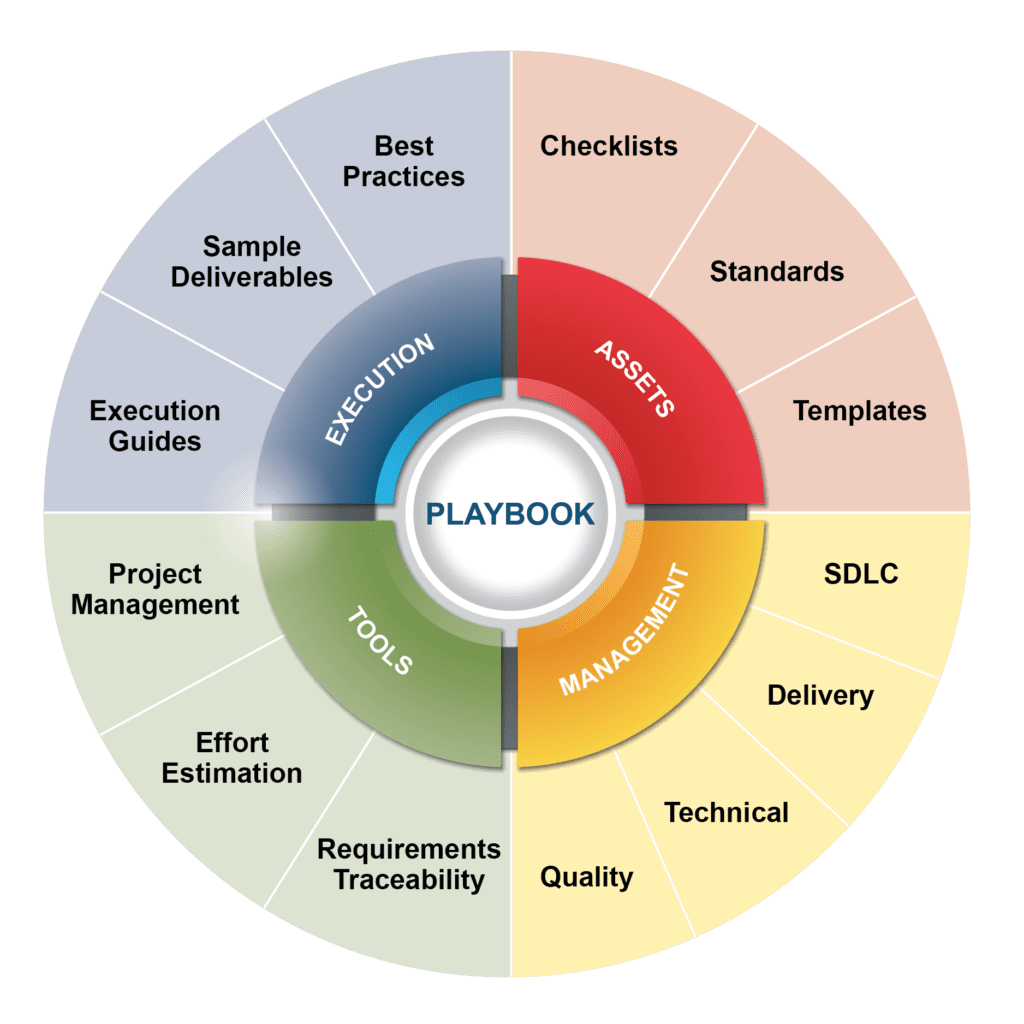
SDi Playbook
The SDi Playbook describes our series of integrated management threads, process areas, and assets for building and delivering quality solutions for our clients. Using the SDi Playbook, various solution modules are synchronized into a single, well-rounded delivery strategy to meet our clients’ specific needs. Our framework is a customized approach, ensuring that transformations are thoroughly, smoothly, and effectively implemented with lasting and engrained benefits.
Through assimilation of industry best practices (CMMI®, SEI, PMBOK®), defense acquisition standards, and execution for clients, our playbook incorporates industry-standard methodologies to produce a roadmap in alignment with our clients’ visions for their organizations. The industry-standard methodologies including Agile, DevSecOps, and Rational Unified Process (RUP) to support our clients’ shift to a modern technology environment.
We drive the adoption and scaling of digital and technology initiatives through the integration of solution delivery lifecycle management (SDLM), delivery management, quality management, and technical management practices into our service strategies and client roadmaps. Our roadmap is flexible, iterative, and focused on increased quality and reduction of risk across our clients’ investment lifecycles—from initiation and development, to deployment and closure.
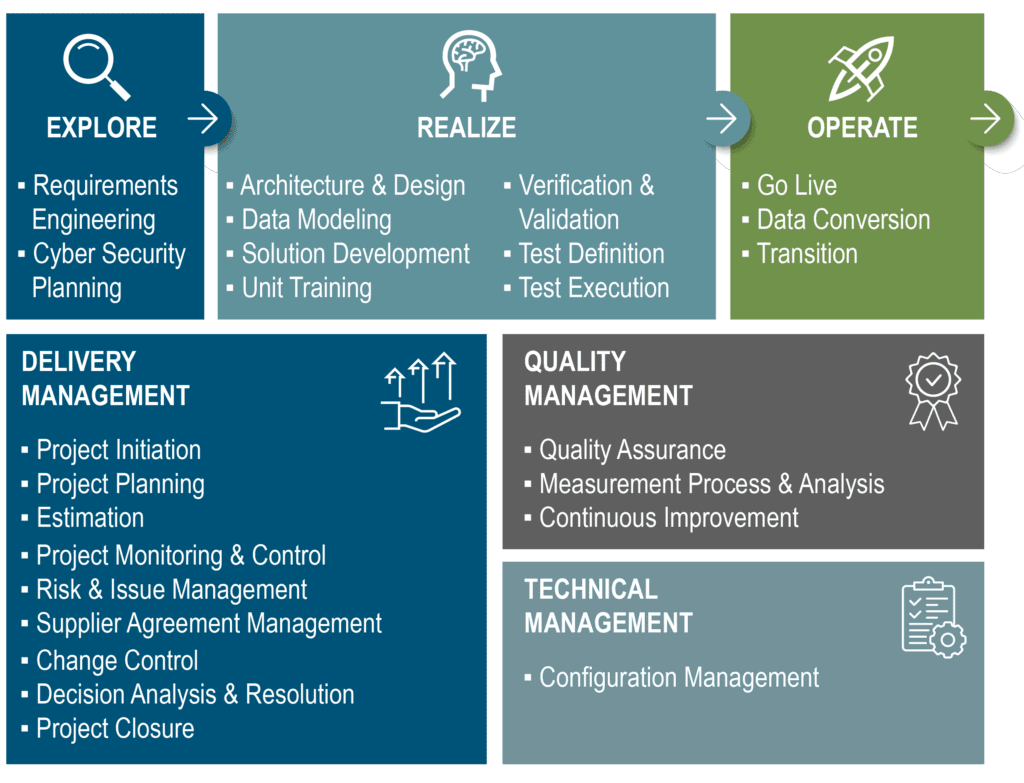
Solution Delivery Lifecycle Management (SDLM)
Through exploration, realization, and operation processes, SDLM encompasses our practices related to project development. These span the full lifecycle of a project, from requirements engineering and cybersecurity planning, to data modeling and solution development and testing, into transition.
Delivery Management
Delivery management describes the various procedures and regular processes that ensure our projects remain relevant to our clients’ needs, on schedule, and efficiently executed. These processes include project initiation, planning, estimation, monitoring and control, risk and issue management, supplier agreement management, change control, decision analysis and resolution, as well as project closure.
Quality Management
The Quality Management aspect of our Method involves continuously monitoring, assessing, and improving the value of our services and output. Our Quality Management (QM) Playbook governs our enterprise-integrated quality program for quality assurance, measurement process and analysis, and continuous improvement practices, ensuring product quality and process quality to meet each project’s unique needs.

SDi’s ISO 9001 Certification
Our ISO 9001 Certification from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) recognizes our dedication to quality in both our internal and external operations. In 2021, we received this honor after a rigorous evaluation process, ensuring that this certification reflects our commitment to quality management. The ISO 9001 reflects SDi’s focus on providing the highest quality service.
Read more about how quality is a cornerstone of SDi’s culture.
Principles of Quality Management
SDi is committed to delivering the highest quality products to our customers. As part of this commitment, our Quality Management System is formed on the basis of seven principles:
The primary focus of quality management is to meet customer requirements and strive to exceed customer expectations. Sustained success is achieved when SDi attracts and retains the confidence of customers and other interested parties on whom we depend. Every aspect of customer interaction provides an opportunity to create more value for the customer. Understanding the current and future needs of customers and other interested parties contributes to the sustained success of SDi.
Leaders at all levels establish unity of purpose and direction, and create conditions in which people are engaged in achieving the quality objectives of the organization. Creating unity of purpose, direction, and engagement enables SDi to align our strategies, policies, processes, and resources to achieve our objectives.
Within SDi, it is essential that all of our people are skilled, empowered, and engaged in delivering value. To be effective, we believe it is important to involve all people at all levels through recognition, empowerment, and enhancement of their knowledge and skills to provide quality.
Consistent and predictable results are achieved more effectively and efficiently when activities are understood and managed as interrelated processes that function as a coherent system. SDi’s Quality Management System is composed of interrelated processes, resources, controls, and interactions, allowing SDi to optimize its performance.
SDi has an ongoing focus on improvement. Improvement is essential for us to maintain current levels of performance, react to changes in internal and external conditions, and create new opportunities.
Decisions based on the analysis and evaluation of data and information are more likely to produce desired results. Decision making can be a complex process, and it always involves some uncertainty. It often requires multiple types and sources of inputs, as well as their interpretation, which can be subjective. It is important to understand cause and effect relationships and potential unintended consequences. Facts, evidence, and data analysis lead to greater objectivity and confidence in decisions made.
SDi’s sustained success is achieved when we closely manage relationships with our customers, suppliers, and partner networks. Our success is achieved through our network’s success.
Technical Management
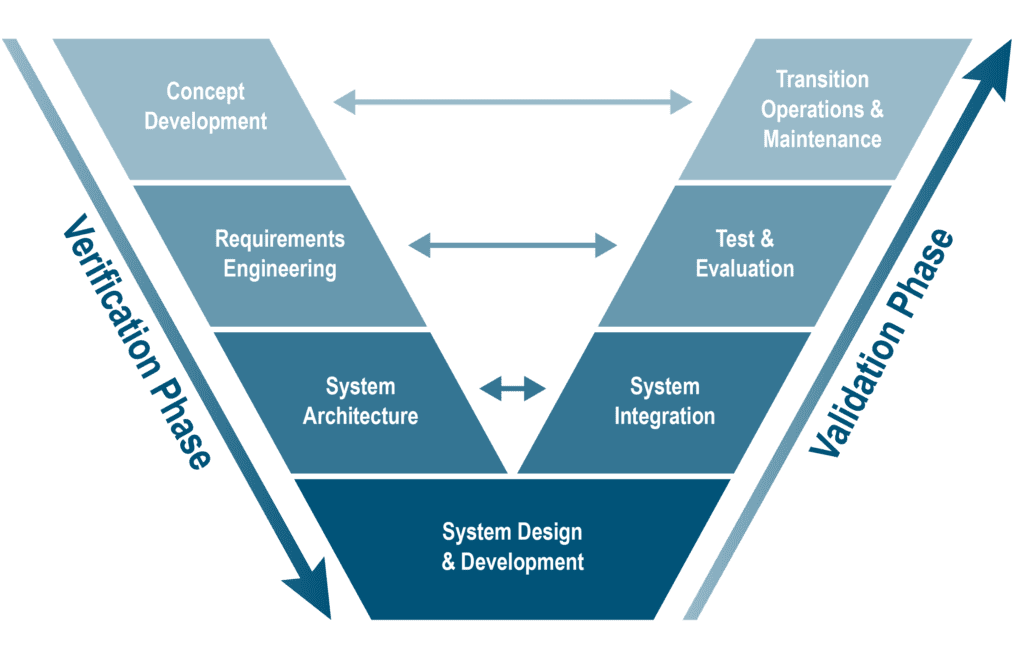
Our project teams are expected to understand and work within these fundamental building blocks for engineering solutions, regardless of the specific project lifecycle methodology used (waterfall, agile, or DevOps).
Our solutions are developed effectively when:
- Solutions are defined conceptually
- User needs are transformed into requirements
- User needs inform how we develop and assess architectures
Our solution teams compose and assess alternative design and development approaches; develop test and certification strategies; monitor and assess efforts in design, development, integration, and test; and assist with field deployment, operations, and maintenance.
All of our systems engineering models and processes are organized around our lifecycle. Although the detailed views, implementations, and terminology used to articulate the SE lifecycle differ across SDi customers, they all share these fundamental elements.